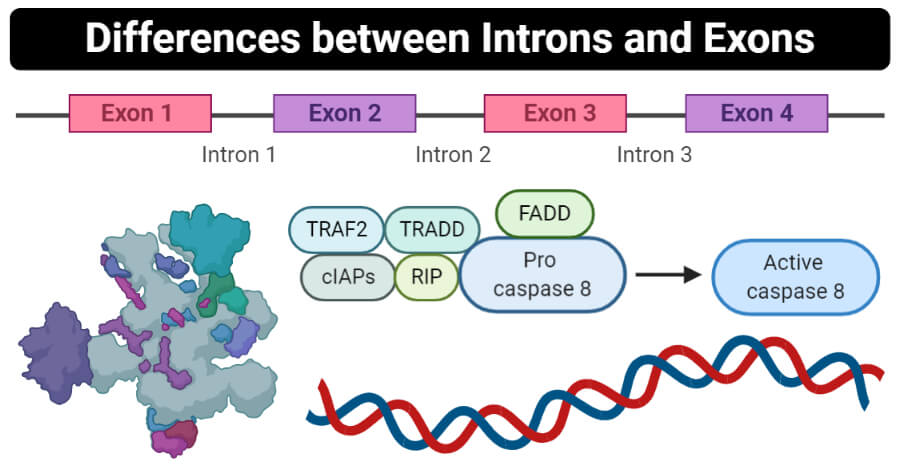
Intron Exon These are non coding sequence of. 1 exons are the coding areas whereas introns are the non coding areas of the gene.
Introns Vs Exons Definition 12 Major Differences Examples
Since its first description researchers in this field have identified and characterized many fundamental elements and.
. 8 rows Introns are the transcribed part of the nucleotide sequence in an mRNA and bound to carry the. Introns and Exons are nucleotide sequences of genes. Answer 1 of 5.
Exons Introns Codons their equivalents. What are the Similarities Between Introns and Exons. The difference between the two.
The difference between cistron and intron. Exons belong to the coding DNA. An exon is any part of a gene that will encode a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing.
Exons code for proteins whereas introns do not. Answer 1 of 3. This will change the peptide sequence of the encoded protein with potential to influence the function of the protei.
Both are present in eukaryotes. Sometimes used interchangeably with the word gene and intron is a portion of a split gene that is included in pre-RNA transcripts but is removed during RNA processing and rapidly degraded. The gene_exon_intron option basically gives you one sequence per gene containing all the of all exons and introns regardless of splicing.
An exon is the part of a gene that codes for a protein. Biology questions and answers. Answer 1 DNA contains genes which in turn are made up of introns and exons.
Introns are the common attribute found in the genes of the multicellular eukaryotes like humans while exons are found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. In the DNA of eukaryotic organisms exons can be together in a continuous gene or separated by introns in. Explain the difference between an intron and an exon.
7 Explain the difference between an intron and an exon. Introns on the other hand. An intron is the non protein coding sequences that interrupt the sequence.
What kind of controls are run in this experiment. Why does a smaller DNA fragment move faster than a larger one. Differences between Exons and Introns.
3 introns are less conserved as their sequences change very frequently over time. Difference Between Introns and Exons Definition. Introns and exons are parts of genes.
Why do the two possible PCR products differ in size by 300 base pairs. The main thing to remember is that exon and introns are features of DNA whereas codons are features of RNA. Both sequences transcribe into pre mRNA.
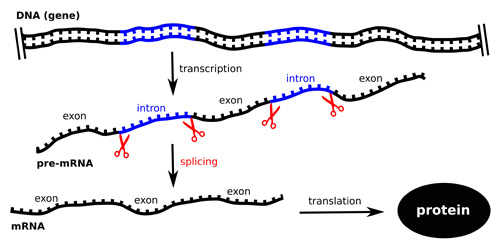
One of the fundamental issues in RNA splicing research is represented by understanding how the spliceosome can successfully define exons and introns in a huge variety of pre-mRNA molecules with nucleotide-precision. Introns or the intervening sequence are considered as the non-coding part of the genes while the exons or the expressed sequence are known to be as the coding part for proteins of the genes. Start studying Intron Exon.
2 exons code for the proteins but the introns are not implicated with the protein coding. Introns and Exons are the genetic material. Exons are made up of stretches of DNA that will ultimately be translated into amino acids and proteins.
Introns belong to the non-coding DNA. They are present in DNA and RNA. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
Even if a gene has two isoforms and they contain mutually exclusive exons you wont know about it using this option. A great way to remember this is by considering introns as intervening sequences and exons as expressed sequences. Is that cistron is the unit of hereditary material that encodes one protein.
An exon is a sequence of nucleic acids that are represented in the m RNA molecule whereas introns are not expressed into into m. Introns are DNA segments which do not encode any amino acid sequence in the coding region. Explain how agarose electrophoresis separates DNA fragments.
Introns increase the opportunity for recombination between two alleles of a gene. Explain the difference between an intron and an exon. It can also be seen that introns are less conserved which means that their sequence changes very.
Exons are coding areas whereas introns are non-coding areas. Introns Vs Exons Definition 12 Major Differences Examples This raises the probability that a crossover will switch one version of an exon for another version found. But the essential difference between the two is that one is made into protein and the other is not.
They are intragenic sequences. 13 rows Introns are present in the DNA and the mRNA transcripts but are not present in mature mRNAs. An exon is termed as a nucleic acid sequence which is represented in the RNA molecule.
Explain how agarose electrophoresis separates DNA fragments. Three common technical terms in molecular genetics exon intron and codon have specific technical definitions but are often miss-used in hurried or short-hand presentations. Why do the two possible PCR products differ in size by 300 base pairs.
An exon is the part of the amino acid sequence that is retained and translated to produce a polypeptide. Hi briefly mutations in coding regions may greatly impact on the organisms phenotype when they are non-synonymous changing the amino acid which the codon codes. On the other hand transcript_exon_intron returns one sequence per transcript.
An intron is the part of a gene that is transcribed into RNA but the sequence is then spliced out so it does not code for any part of the final protein.

Difference Between Introns And Exons Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
What Is The Difference Between An Intron And An Exon Socratic
Difference Between Introns And Exons Definition Characteristics Function Comparison
0 Comments